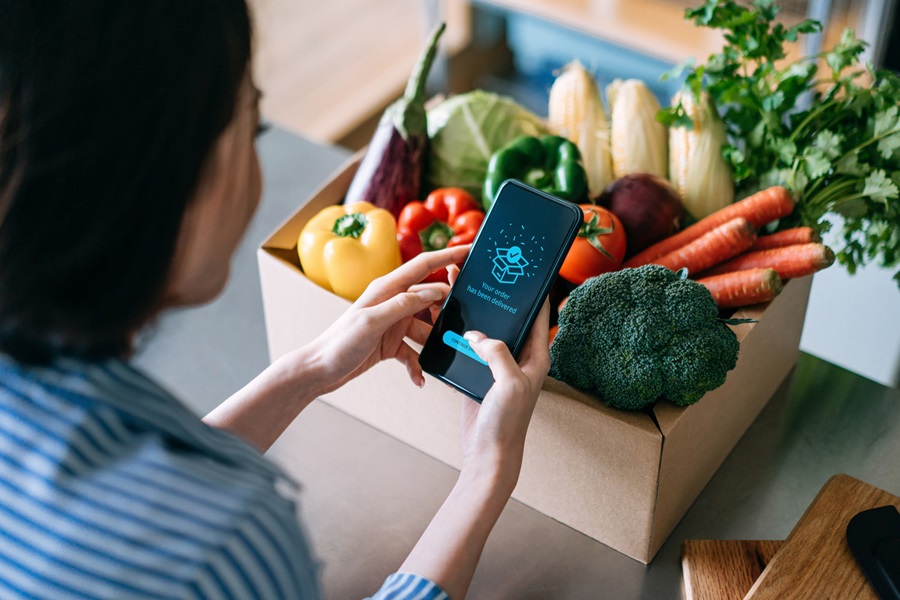
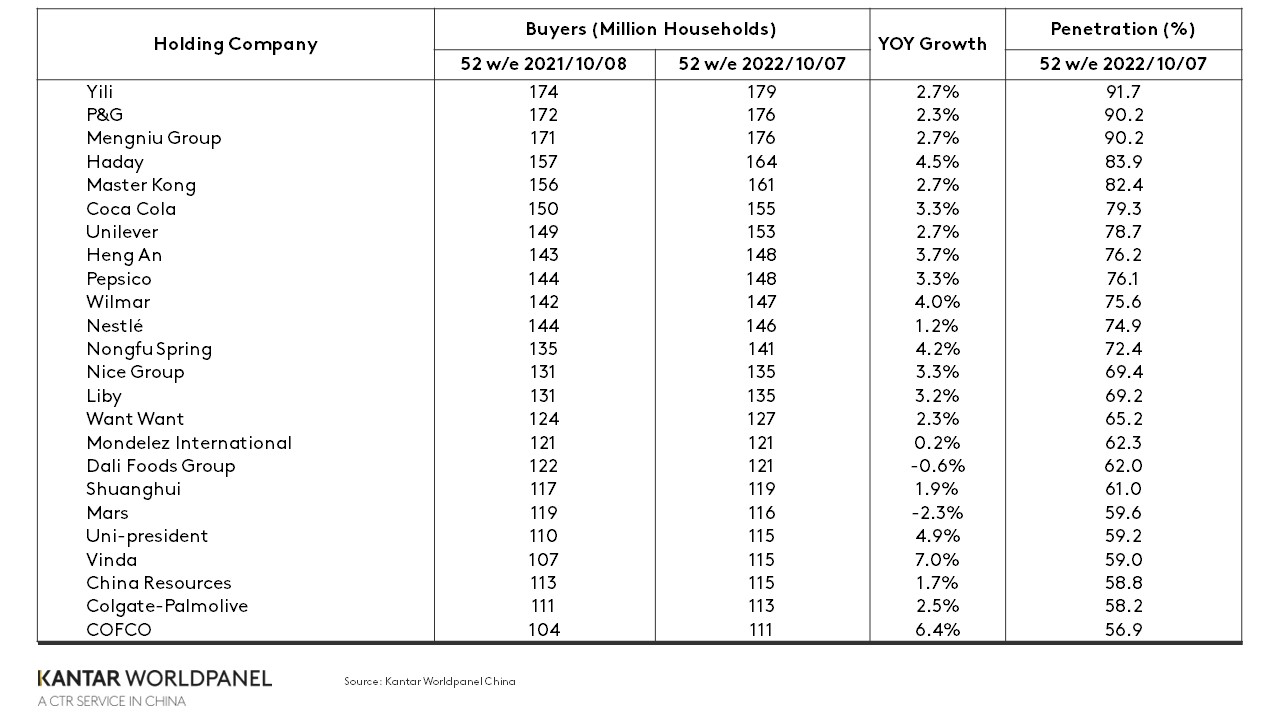
There are now 24 FMCG companies reaching over 100 million households in urban China, according to Kantar Worldpanel data for the year ending 7 October 2022. Compared to the same period last year, these companies added a combined 65 million more consumers to their base, equivalent to a 3.5% growth in households.
The fastest growing players are COFCO, Haday, Wilmar, Uni-president and Nongfu Spring, all food companies, and Vinda and Hengan, both in the home care sector. Driven by the growing popularity of home cooking, Wilmar rose into the top 10 for the first time.
The companies that grew faster than average come mainly from the cooking oil, seasoning, beverage and paper categories, reflecting steady consumer demand during the recent phase of dynamic COVID control in Mainland China.
 Despite the pressure from sporadic COVID outbreaks and supply disruptions, the Chinese FMCG market has continued to demonstrate enormous resilience and growth impetus. In this competitive context the top players have kept innovating by uncovering new occasions, as well as accelerating expansion into new channels and new markets, strengthening their leading positions.
Despite the pressure from sporadic COVID outbreaks and supply disruptions, the Chinese FMCG market has continued to demonstrate enormous resilience and growth impetus. In this competitive context the top players have kept innovating by uncovering new occasions, as well as accelerating expansion into new channels and new markets, strengthening their leading positions.
New occasions in ‘the next normal’
In the new era of zero-COVID controls, home-based consumption thrived. Cooking and sharing culinary skills became a social activity among young consumers. Wilmar and COFCO kept expanding their product portfolios across different categories, and launching new products with healthy concepts, like 0-trans fatty acid variants and products containing natural ingredients to enhance consumers’ quality of life.
With COVID-19 lingering, consumers are looking for indulgence and relief. Beverage manufacturers including Nongfu Spring, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo have attracted more Chinese households in the last year by communicating messages about the comfort and joy they can bring. Alongside driving increased sales of its ready to drink brand Oriental Leaf, a sugar free tea-based beverage, Nongfu Spring launched fusion products such as Sparkling Tea, with its positioning of “real tea leaves, abundant bubbles and low sugar recipe”, bringing sensory pleasure to the Chinese tea drinking culture.
On the non-food side, increased at-home occasions also boosted demand for paper-based home care products. Leading players Vinda and Hengan made an effort to expand paper usage, with Vinda launching a washable kitchen paper that helps consumers to both clean and prepare food, demonstrating higher value through multiple functions. Consumers also kept stocking up on personal care and home care products to stay clean and healthy – and Liby, Nice, PG and Unilever constantly tapped into this trend.
O2O attracts incremental consumers
As traditional ecommerce platforms in Mainland China became saturated, their penetration growth slowed down. During the year ending 7 October, pure online penetration was 87.3%, a slight dip from 88.7% in the same period last year. Meanwhile, the O2O model – where shoppers order online for delivery from offline stores or warehouses – satisfied consumers’ needs across all categories and occasions by connecting a vast user base of internet platforms and physical retail stores. During the 40 weeks ending 7 October 2022, O2O sales value grew by 13.5% compared with the same period last year.
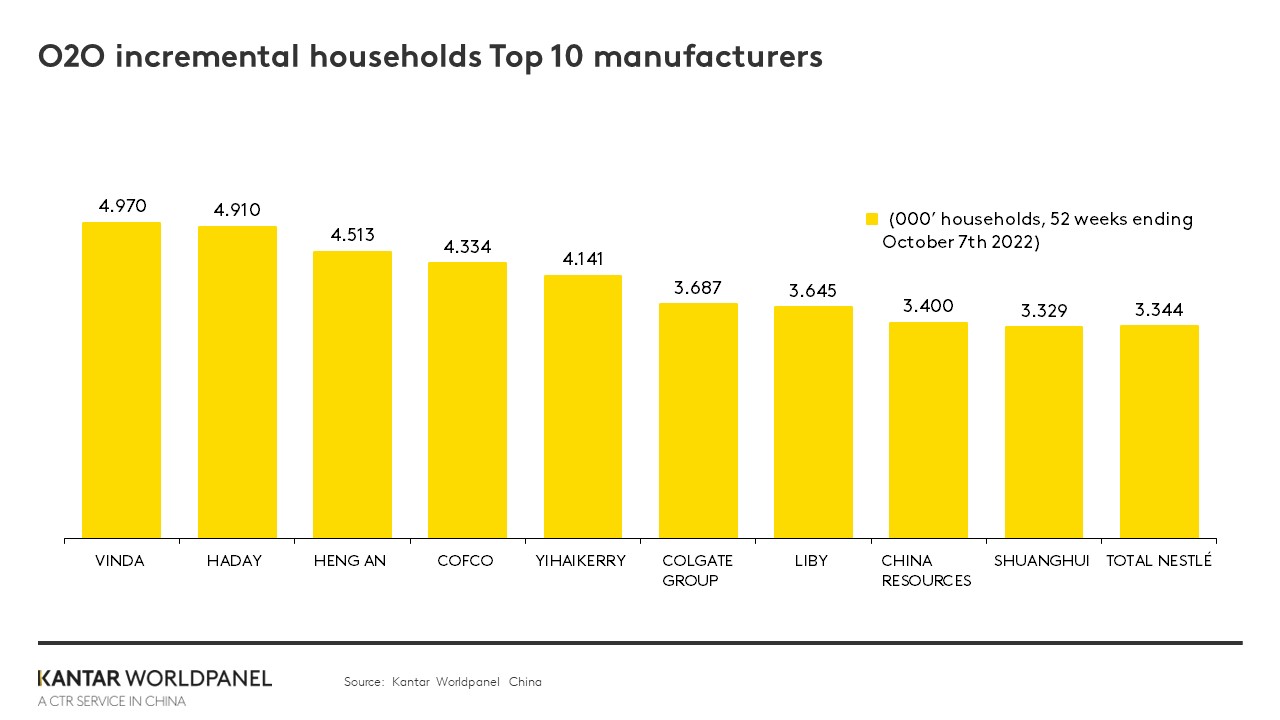
For many brands, O2O has become a channel for reaching more consumers and uncovering new consumption occasions to attract new buyers. Most of the leading players that have generated more incremental shoppers from O2O are food companies. Among these, COFCO leverages O2O to meet consumers’ real-time and convenience needs by delivering daily food supplies to their homes, which has led to an additional 4.3 million new households. Paper manufacturers, like Vinda and Hengan, deliver bulky tissues directly to consumers. Colgate tailors its product offerings to different platforms, for example premium products for O2O marketplaces and mass products for community group buy platforms, which has enabled it to gain more new buyers.
Winning new shoppers in the lower tier
Enhanced brand awareness and lifestyles have made Chinese Mainland vast lower tier cities a critical growth engine for most FMCG companies, contributing 61% of urban China’s FMCG growth during the year to 7 October 2022. As the government introduced greater support, and gradually improved logistics and other infrastructures, the lifestyles and buying behaviours of consumers in the lower tier cities have got closer to those in the high tier cities. In the past 12 months, the total incremental buyers from lower tier cities gained by the 24 companies with the biggest reach accounted for 72% of their total buyer growth.
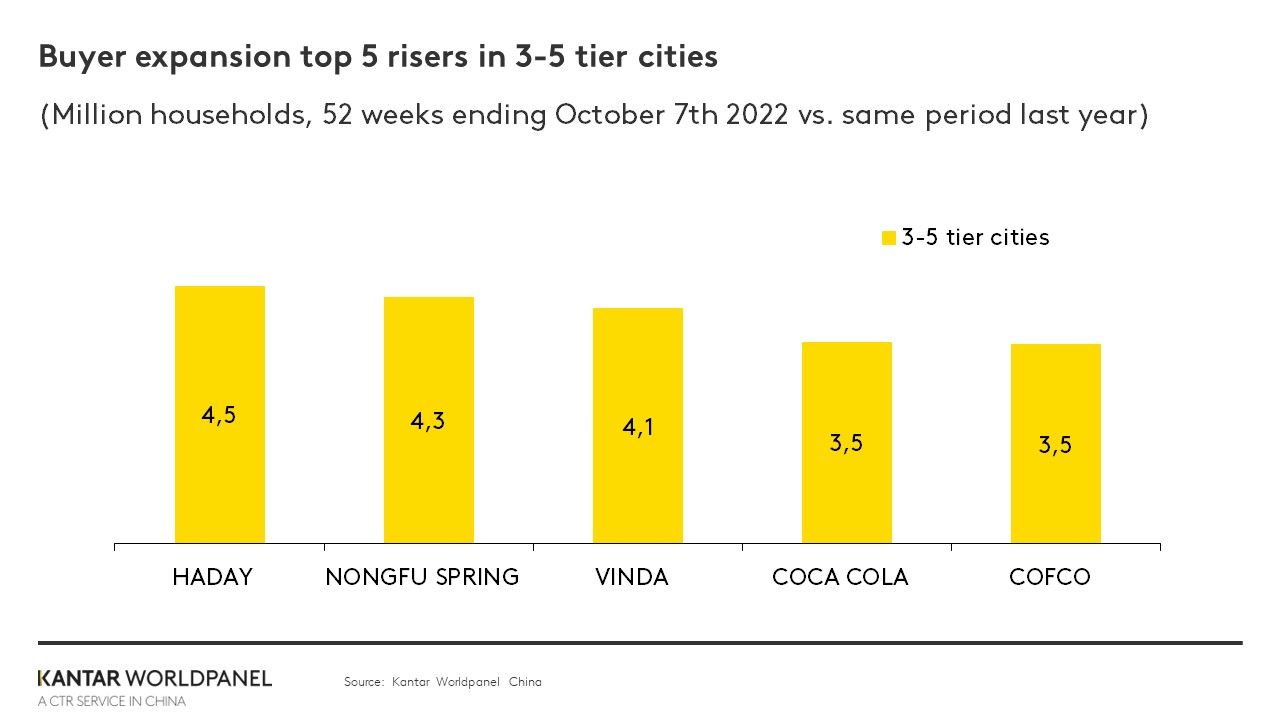
Haday attracted 4.5 million new households in lower tier cities with its successful strategy to focus on small-format stores while driving better availability through ecommerce. Nongfu Spring successfully catered to shoppers’ demands for health and enjoyment, and pushed for increased distribution of its RTD tea in supermarkets and mini-marts. Vinda attracted 4.1 million more households by taking advantage of consumers’ desire to trade up in facial tissues and wet tissues, as well as their emerging online shopping habits.
The needs of Chinese consumers are becoming more diverse. Within this context, FMCG market leaders will need to develop more holistic insights into new occasions to target, develop a clear strategy to win in digital commerce channels, and penetrate deeper into lower tier cities to unlock consistent growth.
If you would like to learn more, please get in touch with our experts or access our data visualisation tool to explore current and historical grocery market data.

